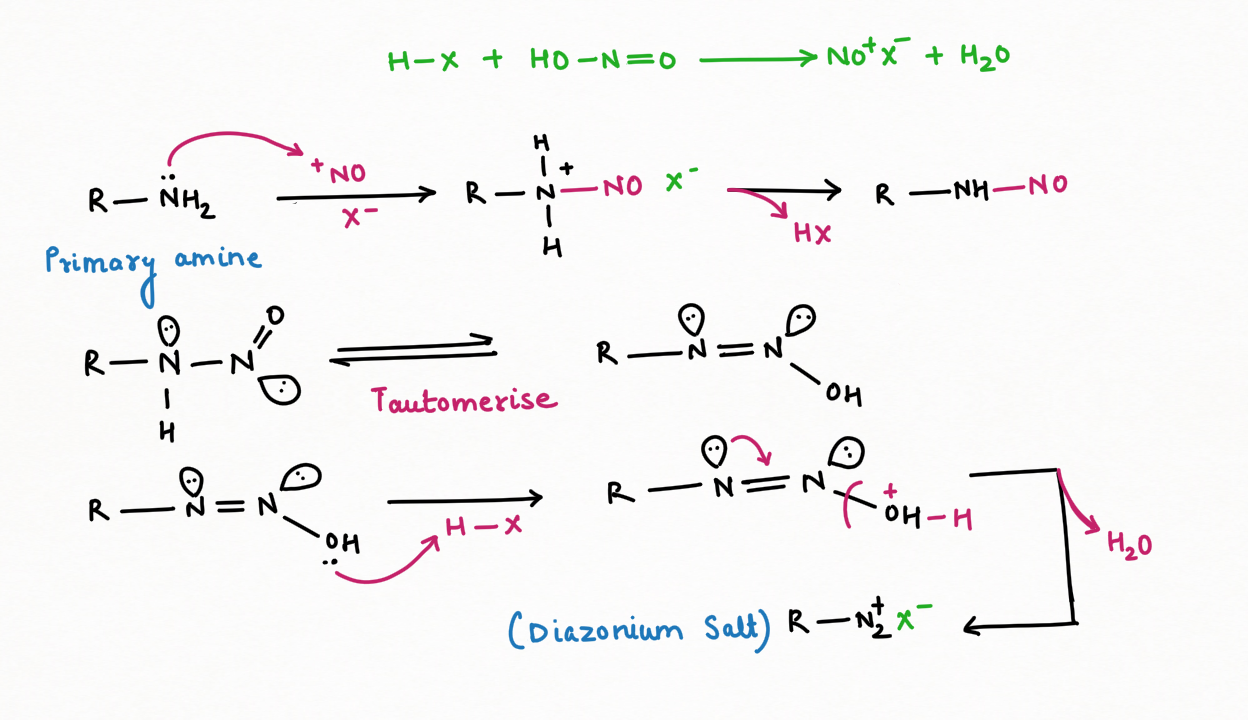
1. Nitrous acid (HNO2) is a good generator of nitrosonium ions:
Nitrous acid is a good producer of nitrosonium ion ( NO+), which performs the reaction of electrophilic substitution of NO+ with an aromatic compound and strong anion. It also produces hydroxide ions which will act as a base for the acidic hydrogen of a substrate, having pka value less than or equal to 25.
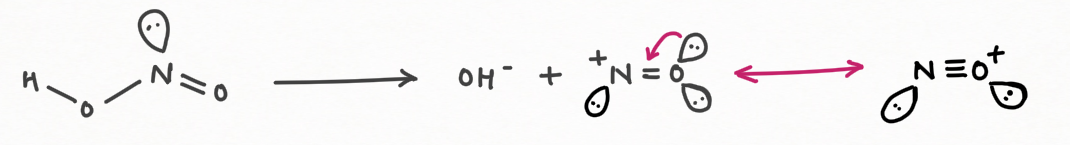
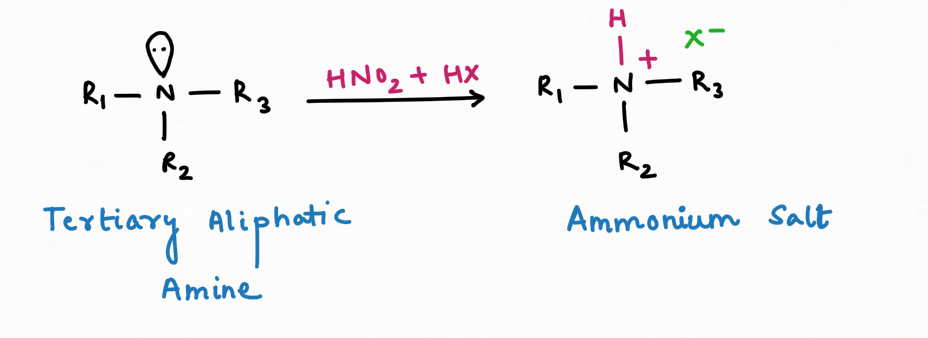
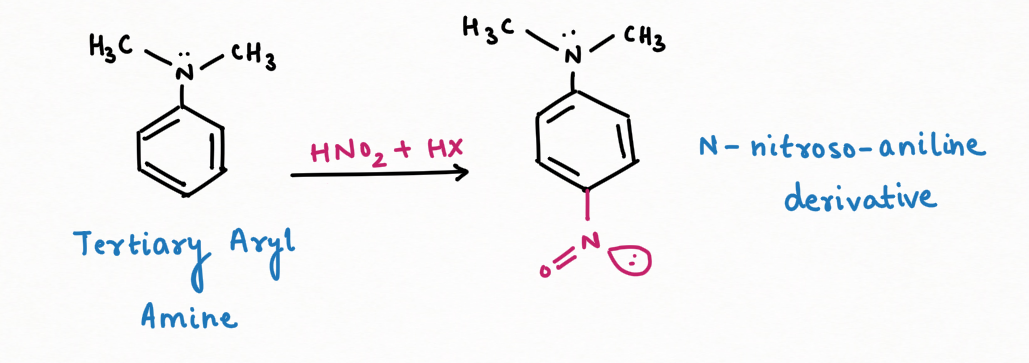
2. Formation of Diazonium salt and reagent for distinguishing among primary, secondary, and tertiary amines.
Primary Amine in the reaction with nitrous acid, will form diazonium salt (N2+)
Further, diazonium may be used as intermediates in a variety of nucleophilic substitution reactions such as dye formation or replacement of nitrogen by X (X= F, Br, I, Cl, OH, H, CN).
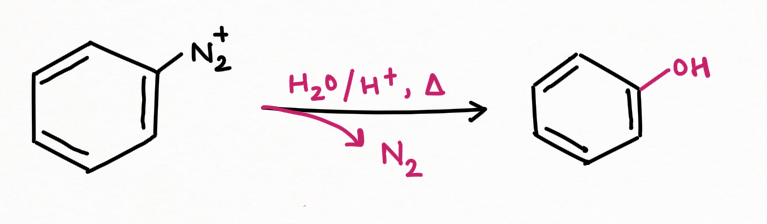
For example, if water is the only nucleophile available for reaction, phenols are formed in good yield.
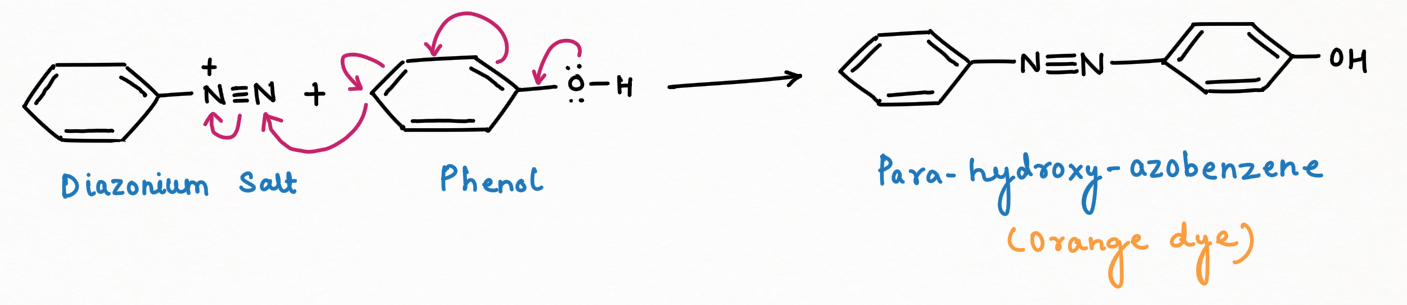
a. Dye formation (Diazo-coupling):
Diazonium salts react readily with phenols, naphthols, and aromatic amines to generate colorful azo compounds. In the azo products, the –N=N– bond connects both aromatic rings, resulting in an extended conjugated system.
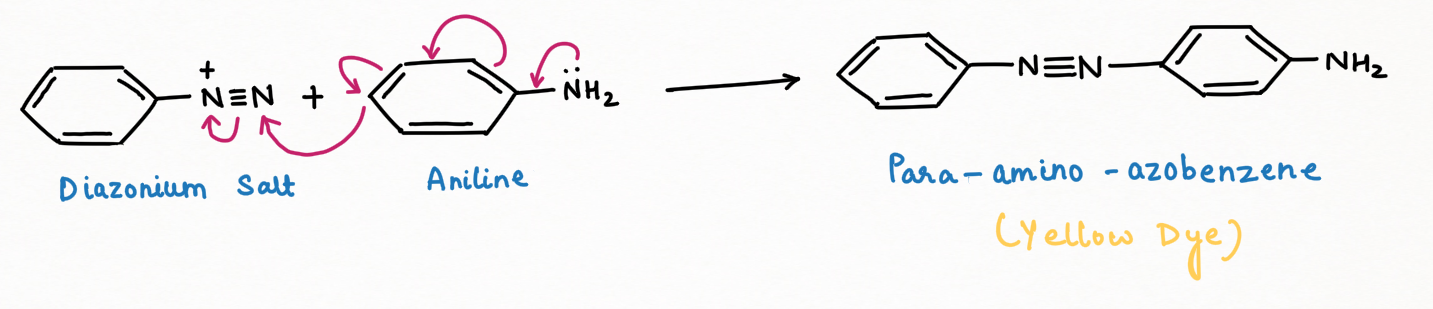
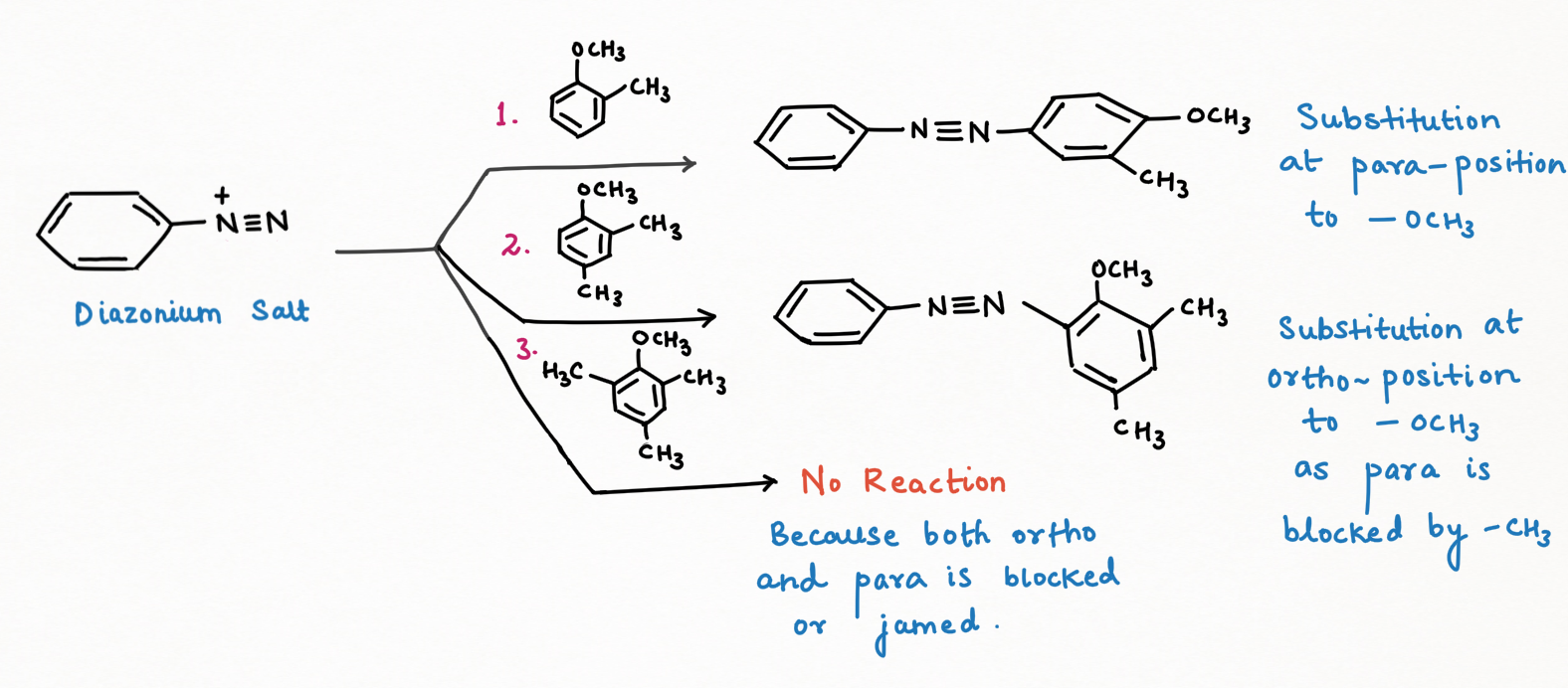
For the best output for dye formation from the reaction between the diazonium salt and benzene derivative, the electrophilicity of diazonium salt can be improved by having an electron-withdrawing group (-M, -H, -I) at para-position to diazonium group, while nucleophilicity of benzene derivative can be improved, having an electron-releasing group (+M, +I, +H) at the para position to which diazonium salt has to be coupled with benzene derivative through azoyde linkage (-N=N-) and also at ortho-position if para-position of benzene derivative is blocked.
The rate of reaction accelerates when the pH rises from 5 to 8. Under mildly alkaline circumstances, phenol functions as a phenoxide ion, which is significantly more activating than phenol itself.
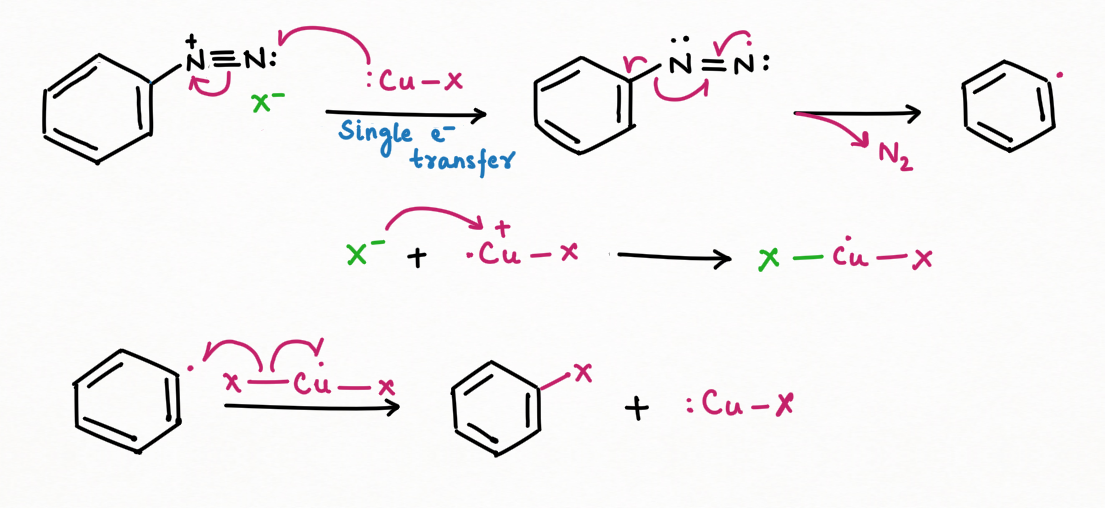
b. Reaction involving the replacement of nitrogen (Organic Synthesis):
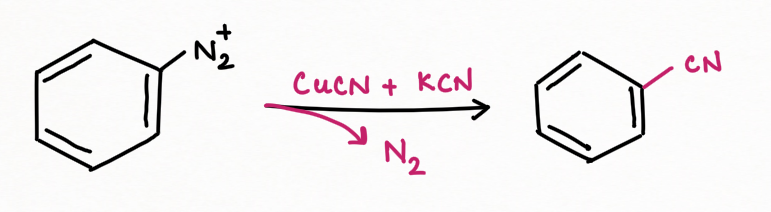
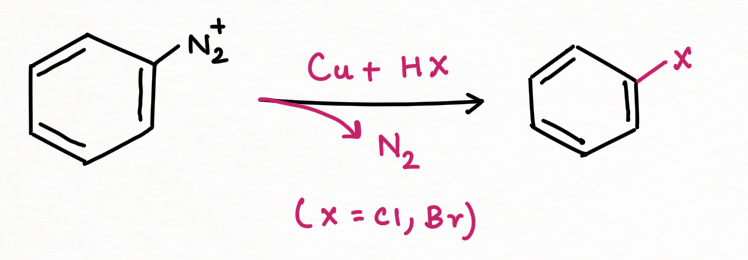
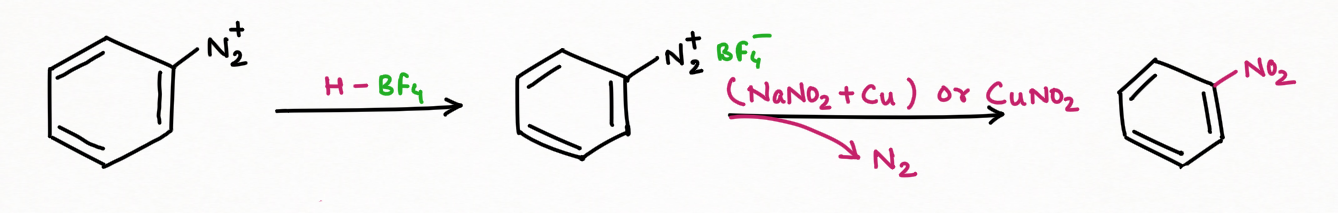
To add F, Cl, Br, I, CN, OH, and H into an aromatic ring, the best general strategy is to replace the diazonium group such as Sandmeyer and Gattermann reaction (replacement by chlorine, bromine, and cyanide).
The formation of nitrogen gas increases the reaction's entropy, favoring the forward reaction and making it irreversible.
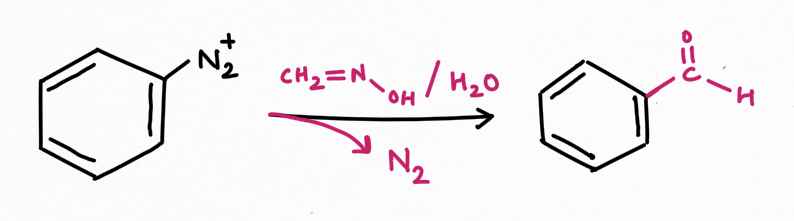
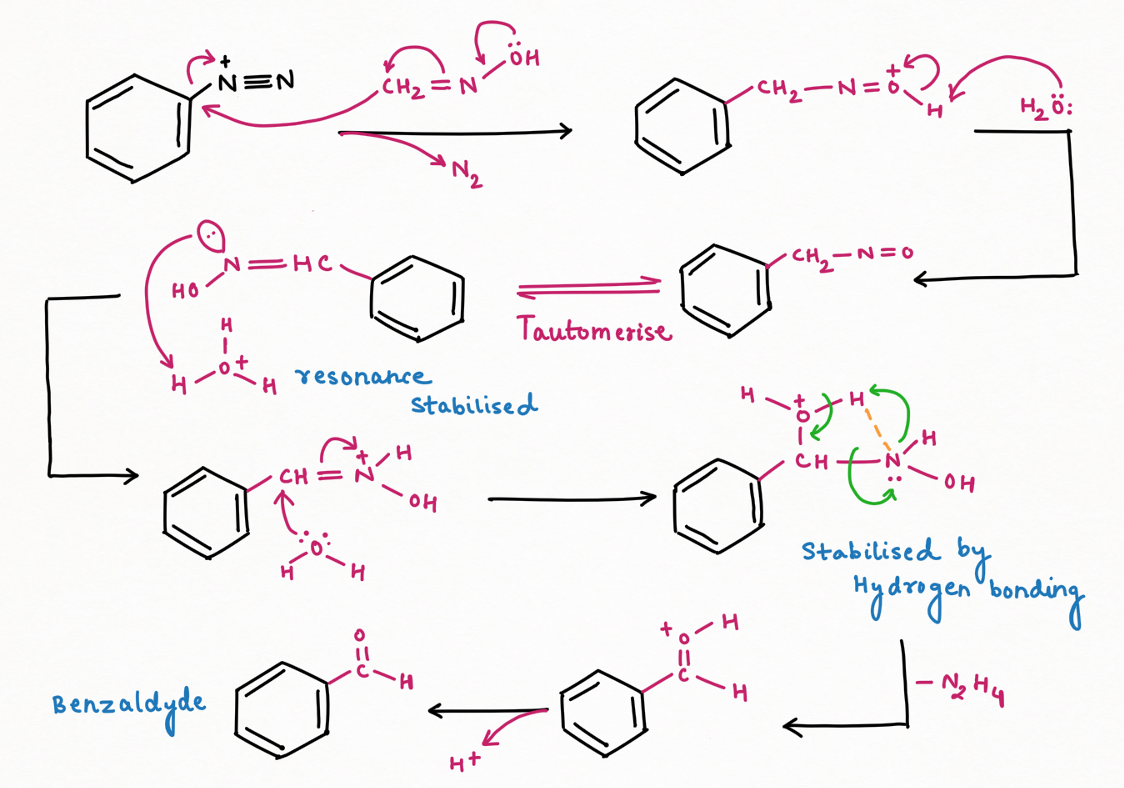
While for replacement by formaldehyde, using formaldoxide followed by hydrolysis:
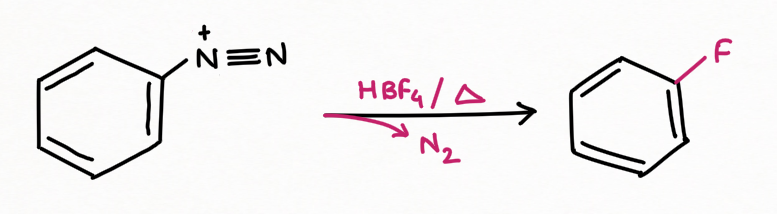
for replacement by a fluorine atom (Balz-Schiemann reaction):
For replacement by cyanide molecule :
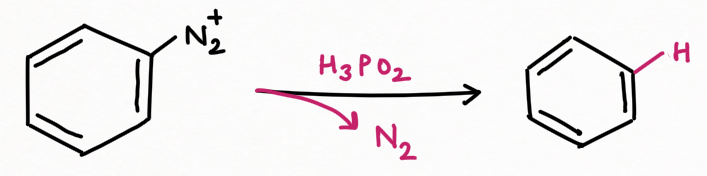
For replacement by hydrogen and hydroxyl group :
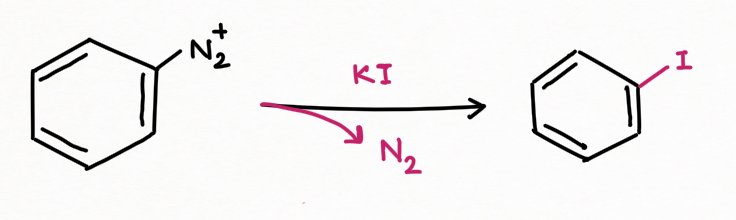
For replacement by Iodine atom using potassium iodide:
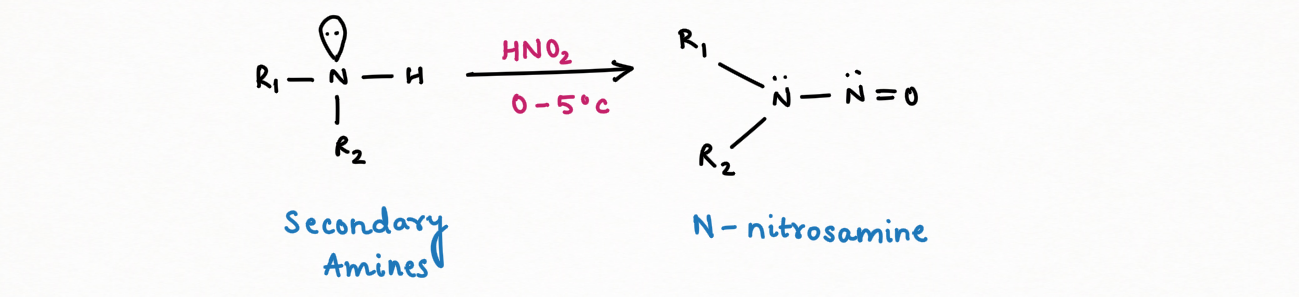
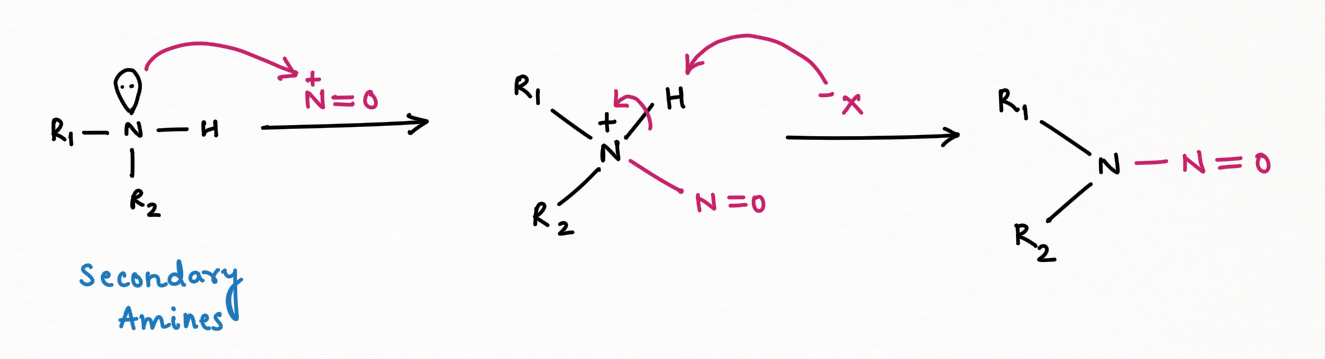
Secondary Amine, in the reaction with nitrous acid, gives N-nitrosamine ( an insoluble yellow mustard oil):
It is interesting to note that N-nitrosamine is a carcinogenic compound.
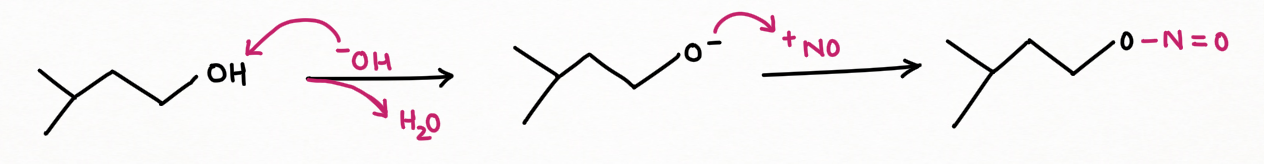
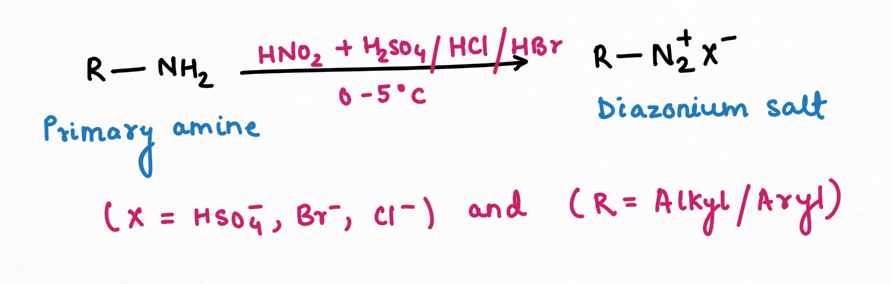
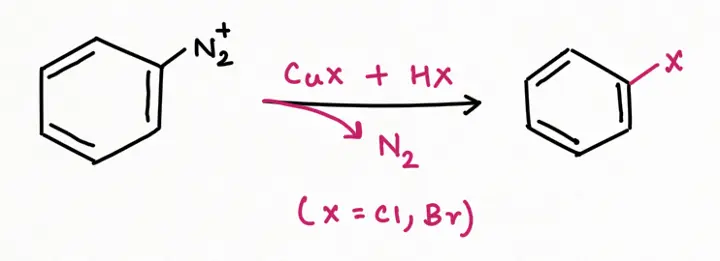
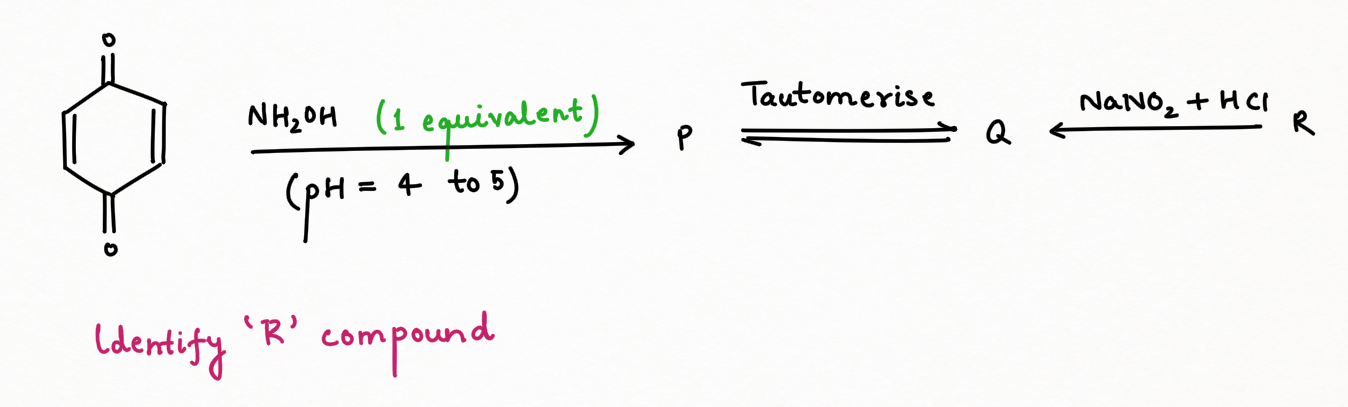
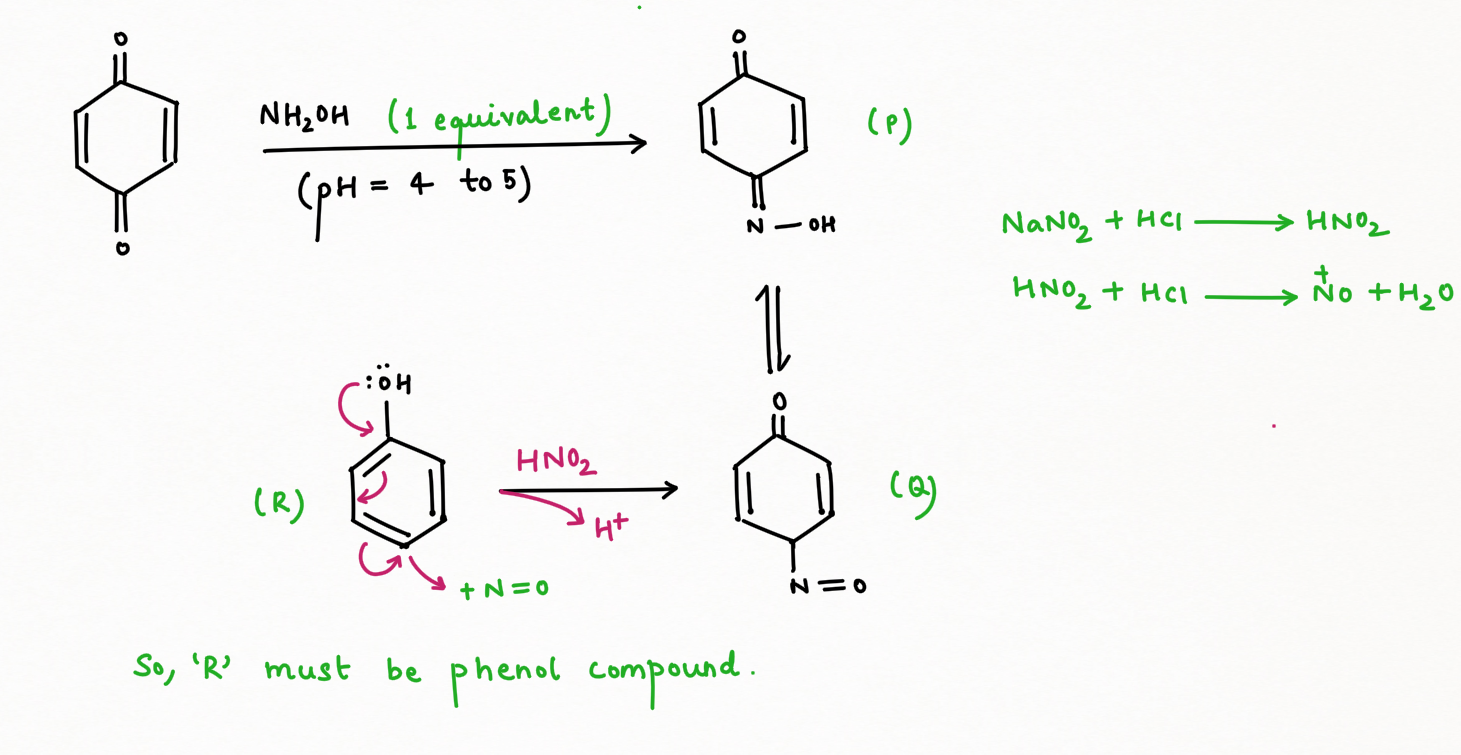
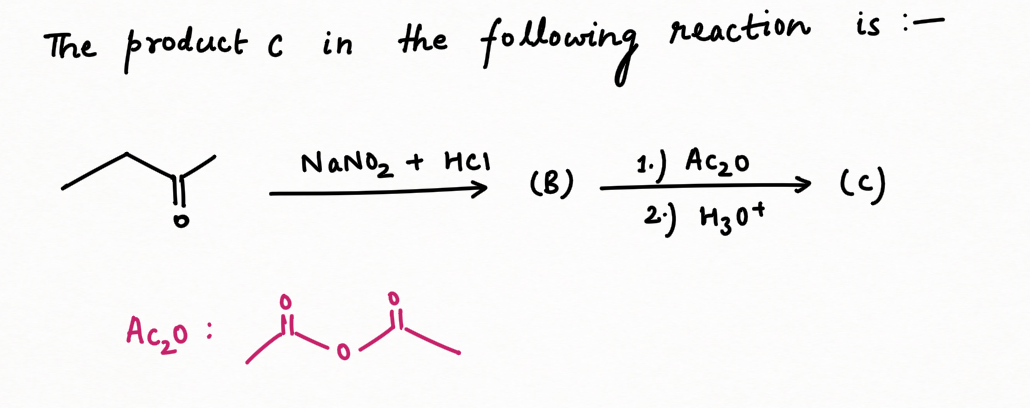
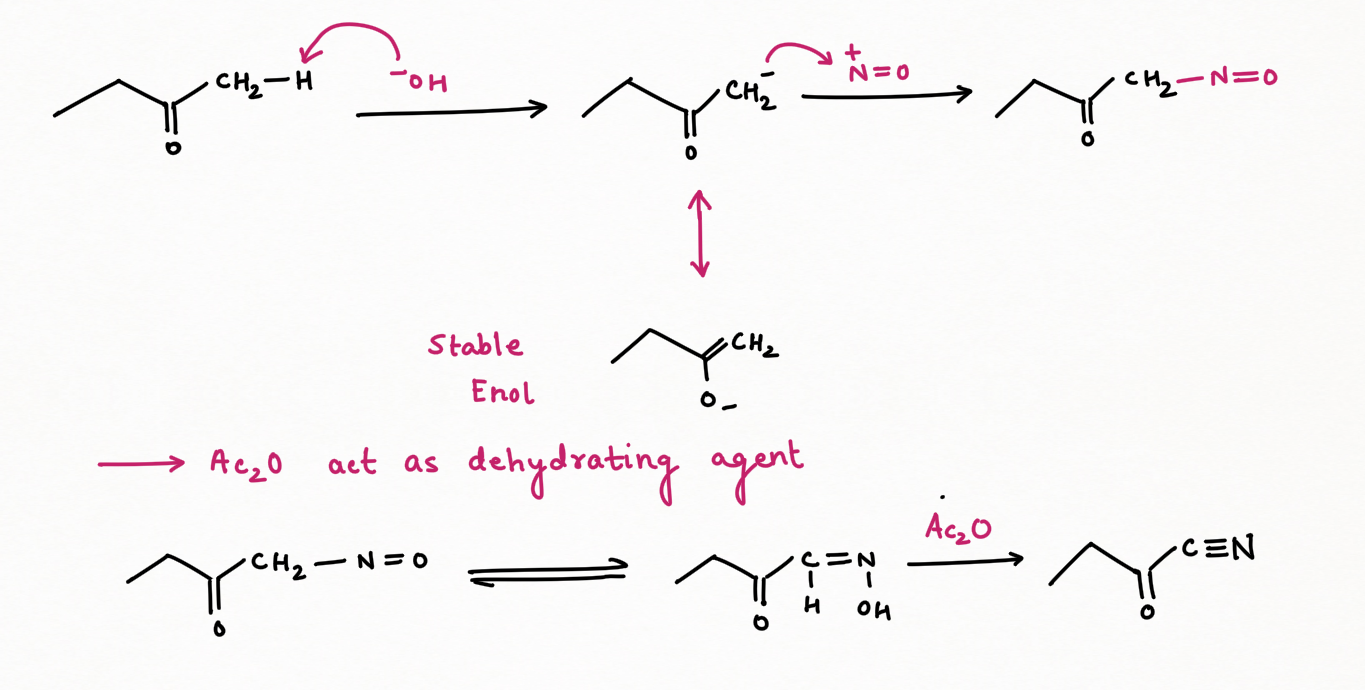
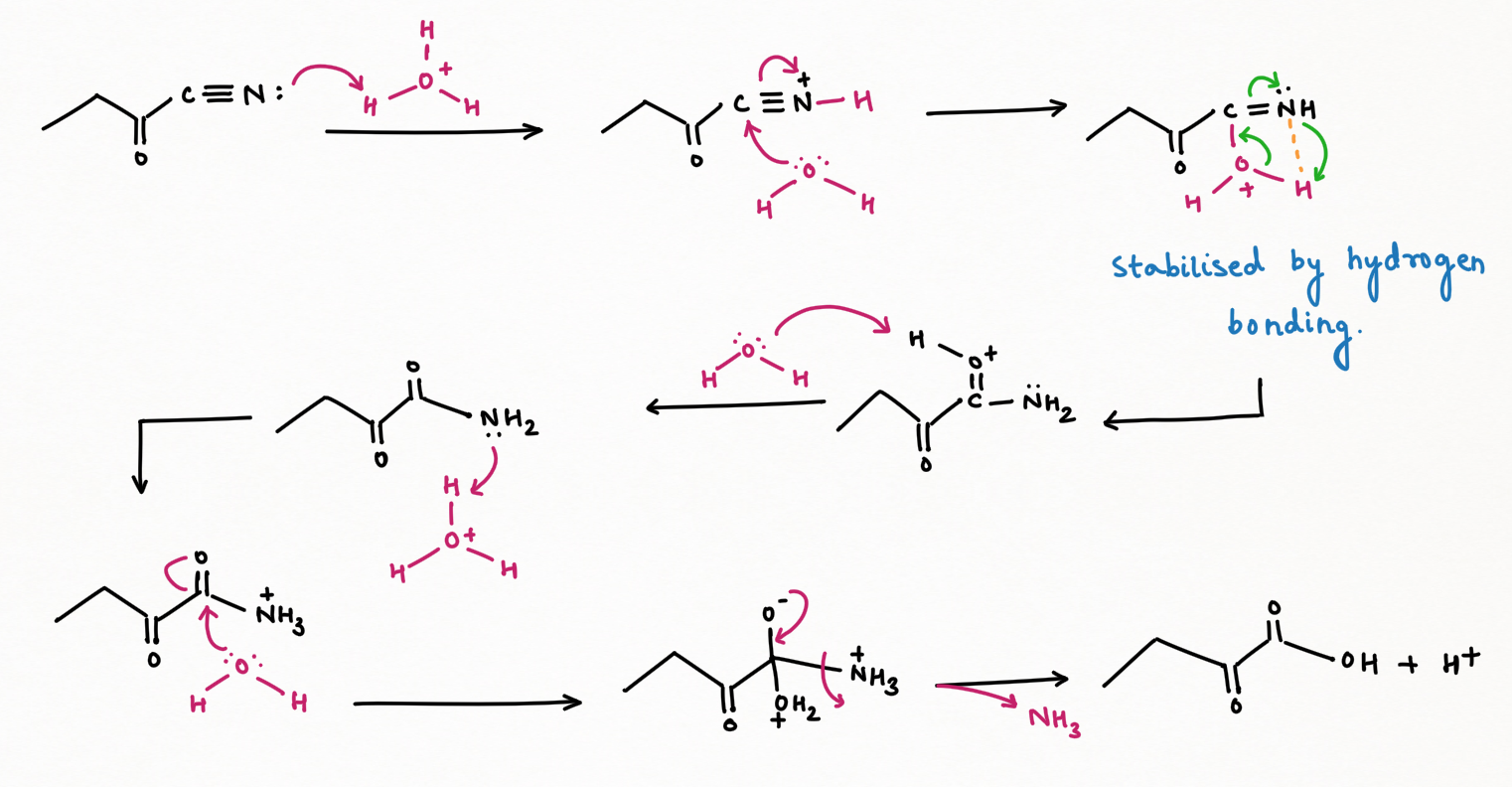
Two application of Nitrous Acid in Organic Chemistry